Incidence-
- Higher in developing countries
- 8% of all intracranial space occupying lesions (SOL).
- About one sixth as frequent as bacterial meningitis
- 0.7% of all neurosurgical operations
Source of infection-
Contiguous suppurative focus
- Direct extension through osteitis /osteomyelitis/ meningitis
- Retrograde thrombophlebitic spread via diploic /emissary veins
- Local lymphatics
Post trauma (3-17.2%)
Hematogenous spread from a distant focus
Cryptogenic origin
Miscellaneous
Stages of abscess formation:
1 Early Cerebritis:
Perivascular inflammation, characterised by Neurutrophils infiltration and some swelling around infection site.
From Days 1-3
- Late cerebritis:
A central area of necrosis develops as the surrounding oedema progresses. There is accumulation of fibroblasts around it
From Day 4-9
- Early Capsule:
Establishment of a ring-enhancing capsule of Well-vascularised tissue with further fibroblast migration
Day 10-14
- Late Capsule:
Collagen fibres and granulation tissue deposits leading to thickening of capsule effectively walling off the areas from surrounding brain.
Day 15 and beyond
Medical treatment-
- Antibiotics- Chloramphenicol, Metronidazole, Sulphonamides, Isoniazid, and Rifampin which penetrate well into normal brain and CSF.
- Staphylococcal brain abscess has shown that the penetration of Vancomycin is excellent; concentration of Vancomycin in the abscess fluid was found to be 80% of the simultaneously obtained serum concentration.
- Pre-operative use of antibiotics would prevent the spread of infection during aspiration or surgical removal of the abscess.
- Selection of antibiotics pre-operatively will be based on the etiology of an abscess and organisms most frequently encountered.
- Later on, after obtaining the culture and sensitivity, proper antibiotics should be started.
- The antibiotics most commonly used are cefotaxime, vancomycin and metronidazole.(effectiveness was 88%)
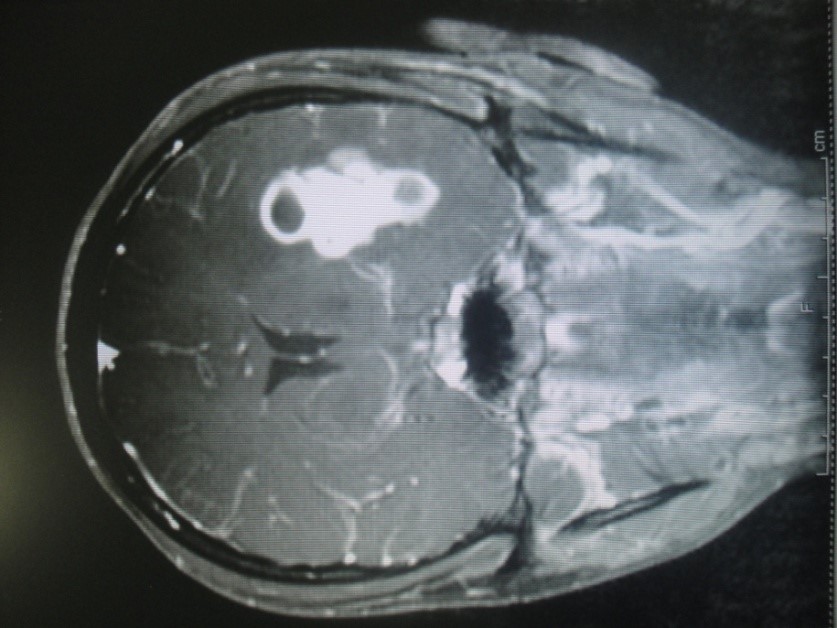
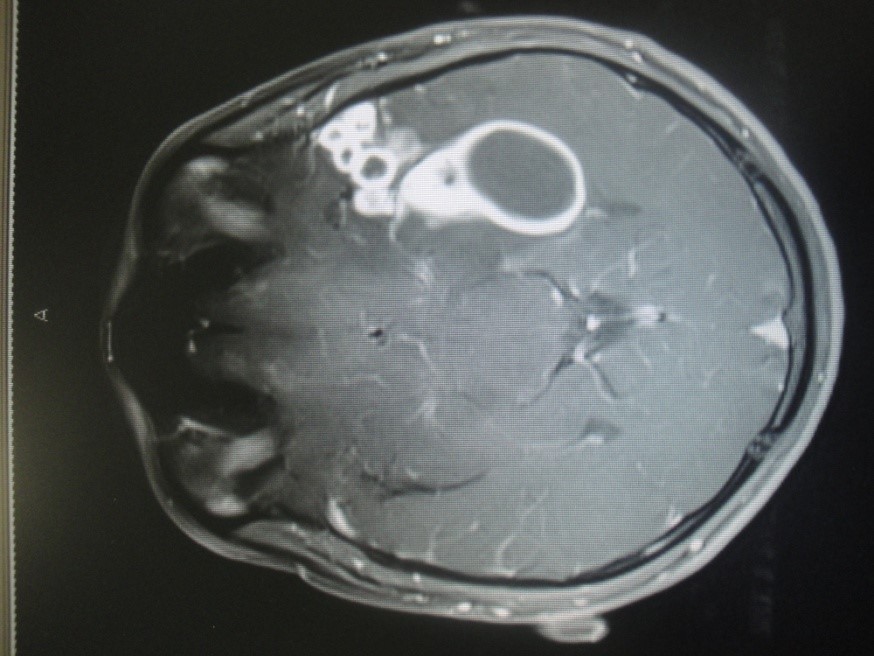
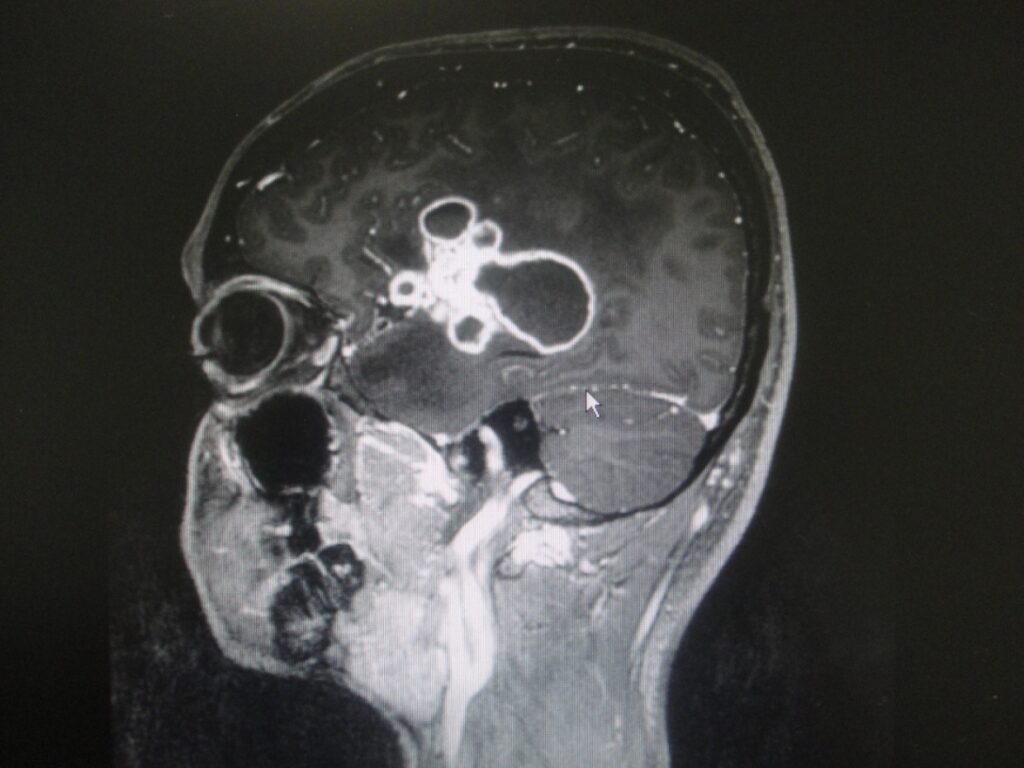
Brain abscess from right ear infection-
12 years / M
Known patient of right ear pus discharge
Headache, fits and fever
MRI Brain showed Right Temporal abscess with right side mastoiditis. (Fig 1 and 2)
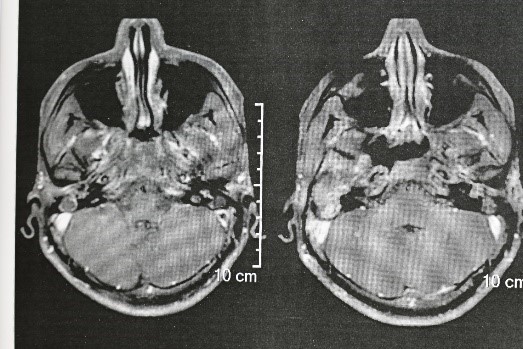
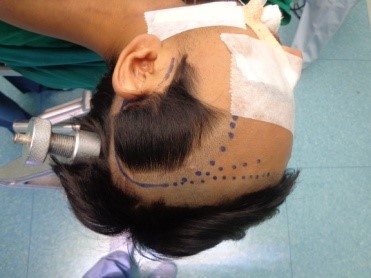
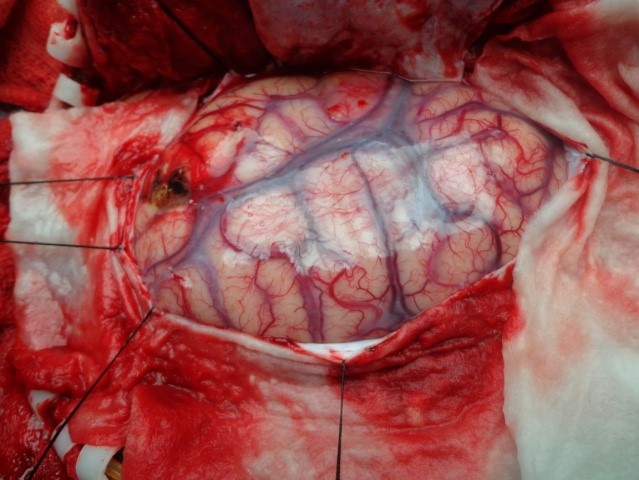
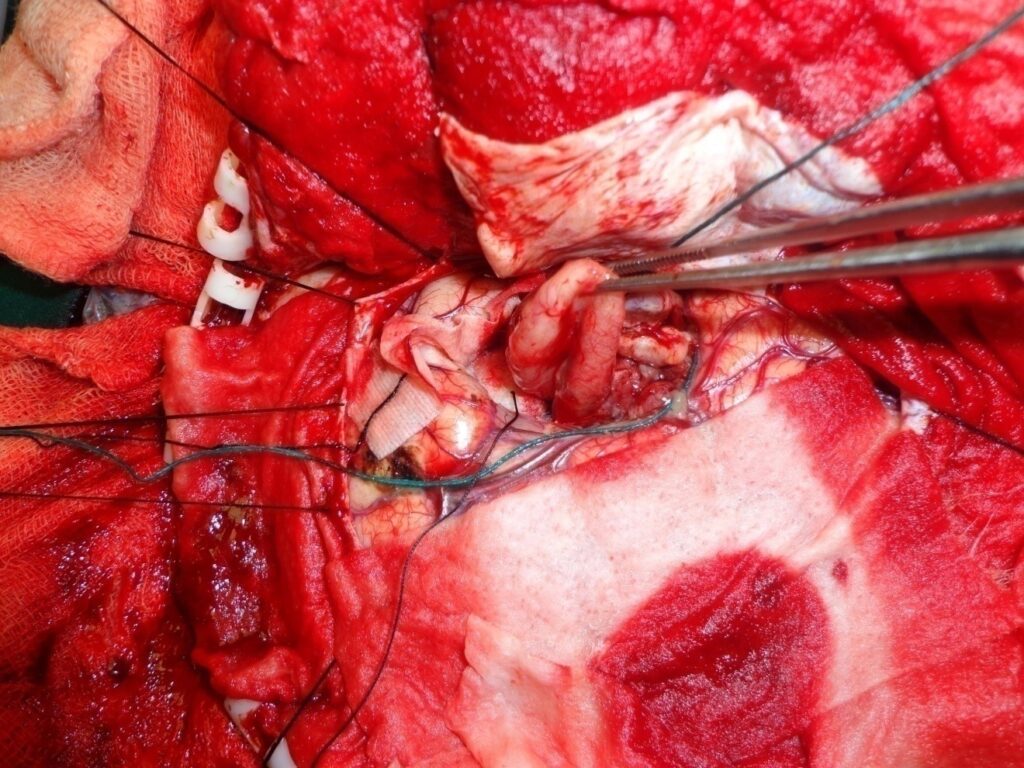
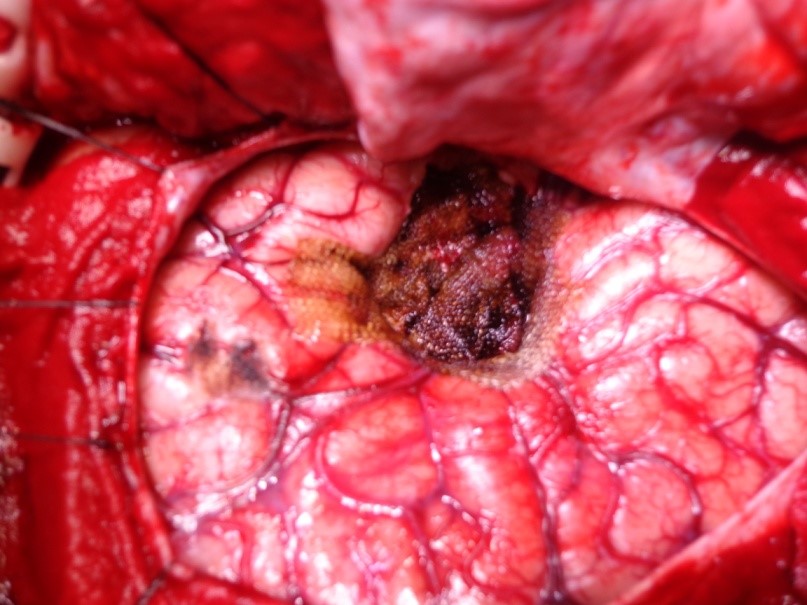
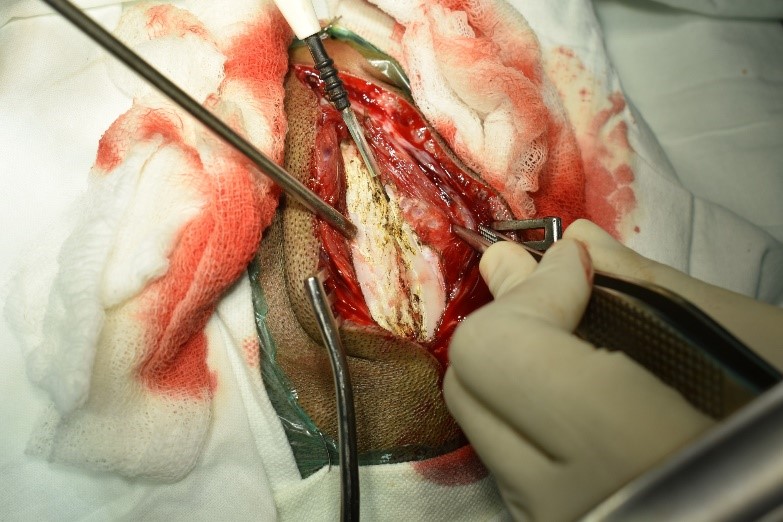
Underwent craniotomy and excision of the abscess (Fig 3-7)
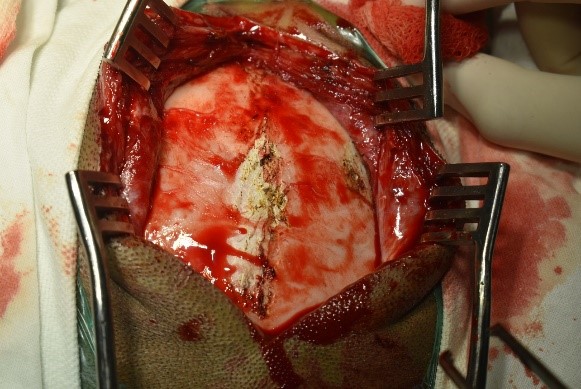
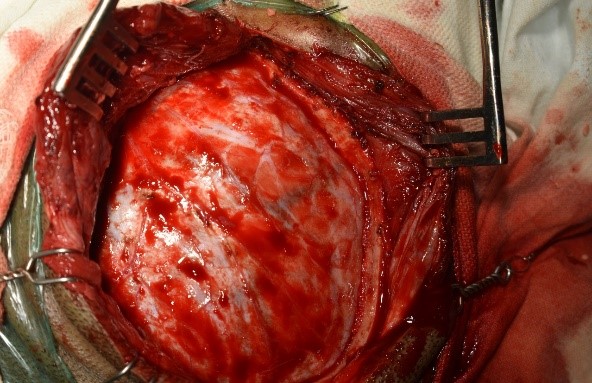
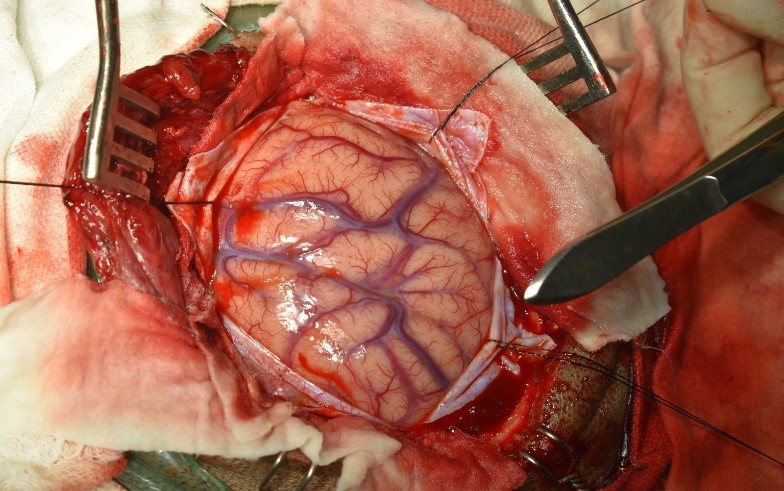
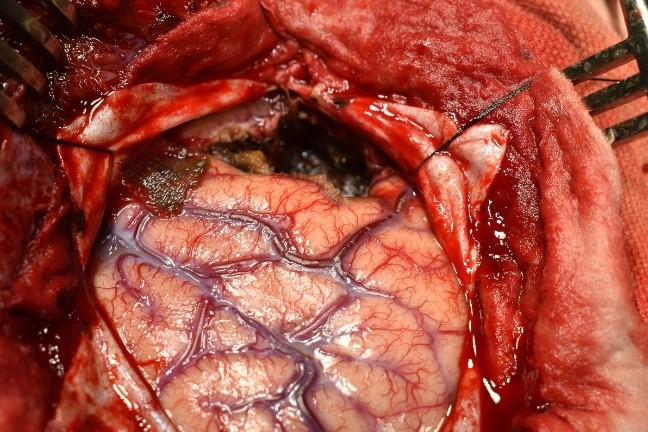
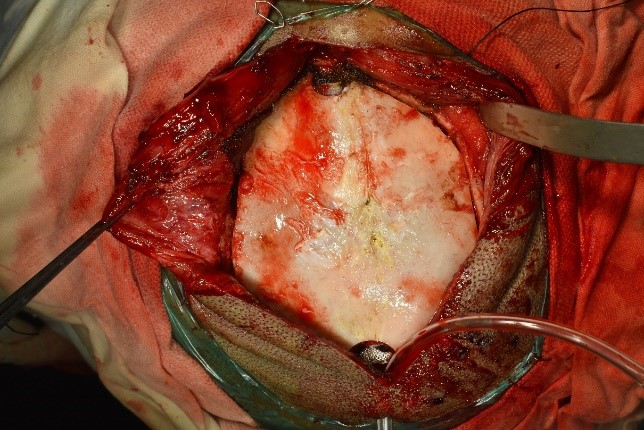
Tubercular Brain abscess
26 M, CA
CNS Kochs
3 yrs of Antikochs, initially responsive later resistant
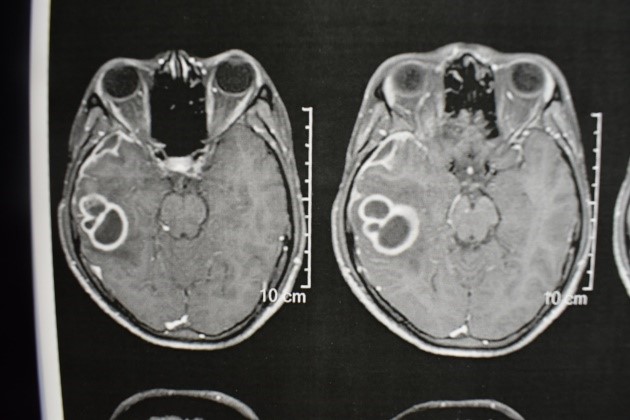
MRI Brain plain and contrast showed multiple left peri-sylvian Tuberculous abscesses. (Fig 1-3)